“Those who can imagine anything can create the impossible.” ― Alan Turing
Before turning to our main topic, let me first decode the term Artificial Intelligence for you(In a very short manner). Artificial Intelligence enabled machines and computers to impersonate the learning, problem-solving and decision-making capabilities of human intellect. So basically AI emphasizes building intelligent machines which are efficient enough for those tasks that require human intelligence!

Source:- Unsplash- Markus Winkler
Did you know that there's a movie based on Turing's test? It's called " The Imitation Game ". It turns around Alan Turing's story, how he joined the cryptographic team and built a machine to crack the German Enigma code! The cast comprises none other than Benedict Cumberbatch (I'm a big fan of this guy), Keira Knightley and many more. Watch this first-class film to see how Turing helped the Brits decipher the cryptic code.

Source:- Pinterest
Now let's turn our point of discussion to the "Alan Turing test" aka "The Imitation game"
Who was Alan Turing?

Alan Mathison Turing was a well-known British mathematician and logician who made primordial contributions to logic, philosophy, cryptanalyst and mathematics. He is popularly thought of as the father of theoretical computer science and artificial intelligence. Turing was fascinated by the ability to mimic intelligence and thought through machines. It was there that his most notable contribution to AI entered the painting, known as The Imitation Game, which later was called Turing Test.
The Turing Test
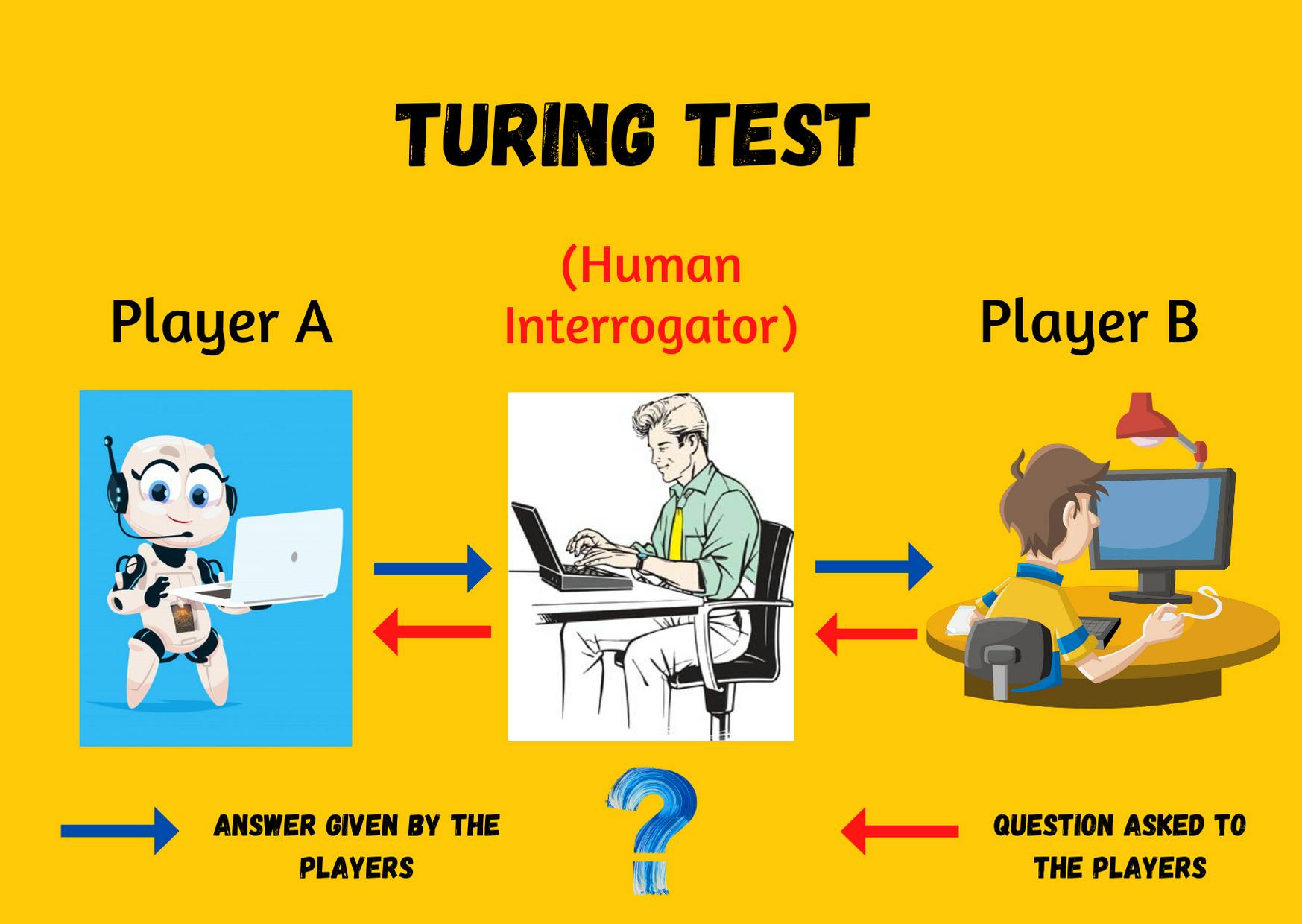
Alan Turing continued to think about a question: "Can a computer talk like a human?". This question led to the idea of measuring AI using the Turing test. He wanted to analyze the machine's ability to manifest sharp behaviour, identical or imperceptible from that of a human. Let's see what exactly it was.
What happened in the test?
Let me make things easier.
We have two players, player A and player B and a human interrogator.
The interrogator will exchange written messages with both players.
The interrogator does not know which player is a computer and which is human.
The interrogator will ask the two players a few questions and observe and analyze their answers.
The interrogator has the primary task to identify a computer and a human amongst the two players.
It's not as easy as you realize! Ha-ha! If the interrogator fails to conclude which player, A or B, is a computer and which is a human, the computer is said to pass the test.
What Turing meant by the test is very much like Forrest Gump's aphorism: "stupid is as stupid does". Turing’s version would be “intelligent is as intelligent says”. By this, he means that an entity is intelligent if one cannot distinguish it from another intelligent entity by observing its behaviour. One limitation of the Turing test as a test of intelligence is that it may actually just measure whether the computer behaves like a human more than whether it is intelligent. We'll see who passed the Turing test in the latter part of the article.
The Chinese room argument

The notion that intelligence is the same as smart behaviour has been questioned by some. To date, the biggest challenge of the Turing test has been John Searle 's Chinese room argument experiment.
To understand this, name the person in the room as Jeniffer and the person outside the room as Alice.
The experiment begins with Jeniffer who does not know the Chinese language and is enclosed in a room with a big manual of the Chinese language.
There is a small mail slot where Alice can drag notes written in Chinese into the room that Jeniffer is in.
Jeniffer receives the note and using the manual provided to her, she tries to find detailed instructions to reply to the notes received from Alice from outside the room.
Searle argued that even if the person outside the room gets the impression that he/she is in a conversation with another Chinese-speaking person, the person in the room does not understand Chinese.
Likewise, even if the machine passes the Turing test and exhibits intelligence, it doesn’t follow that it is intelligent or that it has a “mind” in the way that a human has. The word "intelligent" may be substituted with the word "conscious" and an equivalent argument may be advanced.
Who passed the Turing test?
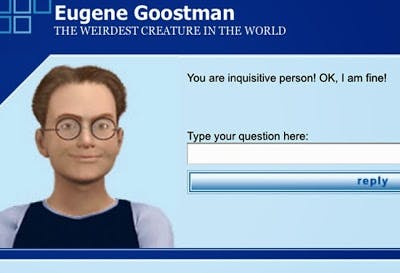
Did Eugene Goostman pass the Turing test?🙂
 Source:- cosmicoblog.com
Source:- cosmicoblog.com
Eugene Goostman is a computer program, which has duped 33% of the judges making them believe he is a 13-year-old Ukrainian boy! To be precise, he easily misled 10/30 judges. He keeps changing the subject and making silly jokes to avoid answering questions. Apparently, Eugene passed Turing's test! To view Eugene's conversation, visit this website.
Did PARRY passed the Turing test? 😔
The answer is No. Unlike the Loebner Prize , which is a Turing Test, PARRY was simply an exercise.
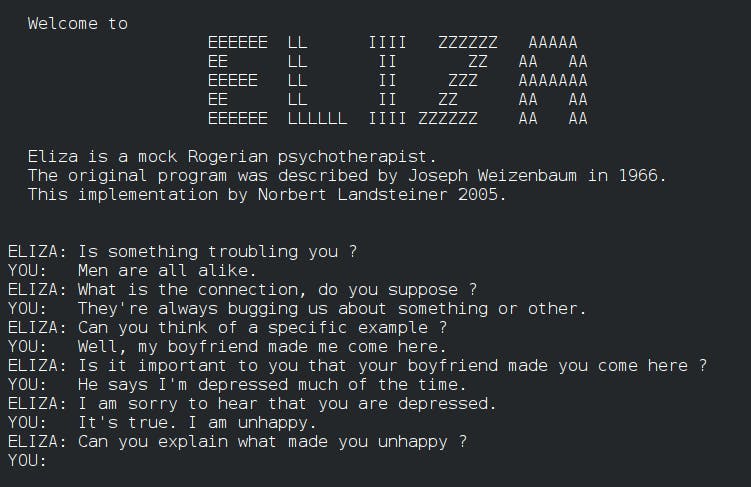
Did ELIZA passed the Turing test? 🙂
 Source:- Wikipedia-Unknown
Source:- Wikipedia-Unknown
Yes. ELIZA has undergone a limited Turing test for machine intelligence. Eliza [Weizenbaum, 1966] was an early AI program and impressed many people who spoke with her.
Did Siri pass the Turing test? 😔
 When it comes to full-blown conversations, Siri fails. Siri only works with simple and short sentences such as "Read my new messages", "Increase brightness" etc. Thus, Siri becomes easily identified as a virtual assistant . In the near future, Siri could also pass the test, but at this time, it fails.
When it comes to full-blown conversations, Siri fails. Siri only works with simple and short sentences such as "Read my new messages", "Increase brightness" etc. Thus, Siri becomes easily identified as a virtual assistant . In the near future, Siri could also pass the test, but at this time, it fails.
Did Alexa pass the Turing test? 🤔
 It can probably pass the test! Unlike Siri, Alexa is always on which means, there is a natural conversation with Alexa that can happen at almost anytime.
It can probably pass the test! Unlike Siri, Alexa is always on which means, there is a natural conversation with Alexa that can happen at almost anytime.
Did Cleverbot pass the Turing test? 🙂
 Yes. Cleverbot passed the Turing Test on September 3, 2011. At the 2011 Techniche festival at the Indian Institute of Technology in Guwahati, judges determined Cleverbot passed for human 59.3% of the time, with a passing score being 50.05% or higher. Cleverbot has a unique feature of learning from conversations it has with humans. Despite Cleverbot passing the Turing Test, there’s still a huge difference between Cleverbot and another human.
Yes. Cleverbot passed the Turing Test on September 3, 2011. At the 2011 Techniche festival at the Indian Institute of Technology in Guwahati, judges determined Cleverbot passed for human 59.3% of the time, with a passing score being 50.05% or higher. Cleverbot has a unique feature of learning from conversations it has with humans. Despite Cleverbot passing the Turing Test, there’s still a huge difference between Cleverbot and another human.
Conclusion
Let me be honest with you, the Turing test was never a test for human-like intelligence. If you do some research on it, you will find that Turing didn't mention it in any of his published papers or via his presentations. This test was just to demonstrate the machine's communication skill. Noam Chomsky had a view that machines can display their intelligence in different possible ways so why did Alan Turing involve human language in his test which is merely one small part of human intelligence. But that doesn't mean the machine is smart or shows human intelligence.
So, in essence, for a machine to pass the Turing test does not mean that the end of humanity is just around the corner!
You can watch my YouTube video on What was the Turing test? by clicking this 👉🏻 link 👈🏻 OR by directly watching it here itself👇

