Table of contents
- Now let's briefly discuss and comprehend what cybersecurity is and how it impacts the world.
- What Cybersecurity Means to Individuals Varies
- Domains
- Frequent cyber threats
- No-trust/Zero trust security policy
- Concerns with cyber security
- Dicey cybersecurity myths
- Cybersecurity: Why It's Important
- New Threats Are Posed by Emerging Technologies
- Cybersecurity advice: How to defend yourself against cyberattacks
“Security should be built in, not bolt-on.”
Some of the biggest changes to the globe since the beginning of humanity have occurred within the span of only one generation. Along with the development of mobile technology and wireless networking, the Internet's accessibility as a tool for both consumers and companies has sparked an Information Revolution that has had an influence on almost every element of human life.

Nevertheless, this dependence on technology has also raised significant vulnerabilities. It appears that there is fresh news about a data breach, cybercrime, or something similar every day. In addition, since humankind's reliance on technology grows everyday, the negative effects of cyberattacks have the potential to become increasingly serious, to the point that individuals may now lose their fortunes, reputations, health, or even their lives as a result of cyberattacks.

Consequently, it should come as no surprise that individuals in the current world are aware of the necessity to safeguard themselves from cyber-threats.
Now let's briefly discuss and comprehend what cybersecurity is and how it impacts the world.
What Cybersecurity Means to Individuals Varies

Although from a pragmatic way cybersecurity might appear to be a phrase that is easy to define, it really means rather various things to different individuals in different contexts, which has led to a very wide range of related rules, procedures, and practices. Let's go through some of the definitions:-
- Individual's opinion: Cybersecurity implies that their digital devices are safe from malware and that just they and those they have given permission to access their personal data may access it.
- Government's opinion: Creating distinct data categories, that have their own set of corresponding laws, regulations, processes, and technology, may be a component of cybersecurity.
- Shared service providers: Cybersecurity may entail protecting numerous data centers that house numerous servers that, in turn, host many virtual servers belonging to many different organizations.
Let me now share with you my perspective on this:
Networks, devices, programs, and data are all protected from attack, damage, and illegal access by a variety of technologies, procedures, and methodologies collectively referred to as "cyber security." Information technology security is another name for cyber security.
Bottom line: Whilst term "cybersecurity" is simple to define, people's pragmatic aspirations that arise when they encounter the phrase differ considerably. Technically speaking, information security includes the protection of all kinds of data (for instance, safeguarding a paper file and a filing cabinet), although cybersecurity focuses on information and information systems that maintain and process data in an electronically.

Despite this, the phrases are frequently used interchangeably nowadays, with references to cybersecurity being made to aspects of information security that aren't actually included in the latter. Such usage is also a result of the frequent merging of the two. Technically speaking, despite the fact that a person's actions can have major cybersecurity ramifications, if anyone puts down a password on a piece of paper and keeps the paper on his desk where many other people can see it rather than putting it in a safe or safe deposit box, he has breached an information security principle, not a cybersecurity one.
Domains

Layers of defence are included in a solid cybersecurity plan to combat cybercrime, such as attempts to access, modify, or delete data; demand money from users or the company; or obstruct regular business activities. Countermeasures ought to focus on:
Application security: Processes that aid in protecting cloud-based and on-premises apps. Applications should be developed with security in mind from the beginning, taking into consideration user authentication, data handling, and other factors.
Information protection: Your most sensitive data is protected by data protection procedures like the General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR, which prevent unauthorised access, disclosure, or theft.
Client education: Increasing security awareness within the company to improve endpoint security. Users can be taught, for instance, to discard dubious email attachments and steer clear of unidentified USB devices.
Security for vital infrastructure: Techniques for safeguarding the networks, computer systems, and other assets that society depends on for economic viability, public safety, or both.
Frequent cyber threats

Security holes are always being closed by cybersecurity experts, but attackers are constantly seeking new methods to avoid detection by IT, get around defences, and take advantage of flaws that are appearing. The most recent cybersecurity risks are reinventing "existing" risks by utilizing work-from-home settings, remote access technologies, and new cloud services. Among these rising threats are:
- Phishing / social engineering

Users are tricked into disclosing their own PII or sensitive information through the practice of phishing, a type of social engineering. Phishing schemes solicit for classified information, such as login credentials or credit card information, through emails or text messages that look to originate from a reliable organization. The rise in pandemic-related phishing has been reported by the FBI and is associated with the expansion of remote employment.
- Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks

DDoS attacks aim to bring down a server, website, or network by flooding it with traffic from several synchronised systems, typically. Using the simple network management protocol (SNMP), which is used by modems, printers, switches, routers, and servers, DDoS assaults take down business networks.
- Advanced persistent threats (APTs)

An APT is when a hacker or group of hackers infiltrates a system and goes unnoticed for a long time. In order to eavesdrop on corporate activities and collect important data without setting off defensive countermeasures, the intruder leaves networks and systems untouched. An APT is exemplified by the most recent Solar Winds penetration of US federal networks.
- Man-in-the-middle attacks
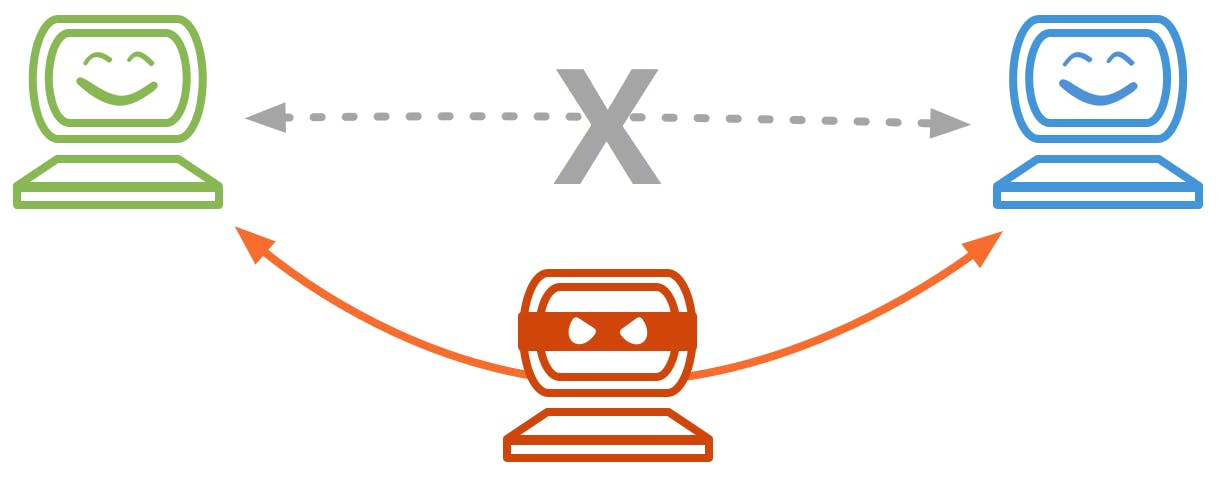
An eavesdropping technique known as "man-in-the-middle" comprises a cybercriminal intercepting and relaying communications between two parties in order to steal data. An attacker may, for instance, collect data passing between a visitor's device and an insecure Wi-Fi network.
- Insider threats

Anyone who has had access to systems or networks in the past, including current or former employees, business partners, contractors, or other individuals, might be regarded as an insider threat if they misuse their access privileges. For conventional security measures that concentrate on external threats, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, insider dangers may go undetected.
- Malware

Malicious software variations, such as worms, viruses, Trojan horses, and spyware, that grant illegal access or harm a computer are referred to as "malware." Attacks by malware are becoming more "fileless" and are intended to avoid common detection techniques, including antivirus software that checks for harmful file attachments.
I will discuss more about these threats in my upcoming articles.
No-trust/Zero trust security policy

Today's businesses are more linked than ever. Different environments are where your systems, users, and data all reside and function. The complexity of installing security controls inside each environment makes perimeter-based protection insufficient today. Degraded protection for your most valuable assets is the end outcome in both situations. A zero trust approach assumes that there has been compromise and implements controls to verify the legitimacy and purpose of each person, device, and connection to the organisation. Organizations require a method for combining security data in order to provide the context (device security, location, etc.) that guides and enforces validation controls if they are to successfully implement a zero trust approach.
Concerns with cyber security

A company must coordinate its efforts across every aspect of its information system to provide successful cyber security. Cyber elements include anything listed below:
- Network security is the process of defending a network against invasions, assaults, and unauthorised users.
- Application security: To make sure that these applications are safe from assaults, apps need to be updated often and tested.
- Endpoint security: Remote access is a must for business, but it can potentially compromise data security. The technique of securing remote network access is known as endpoint security.
- Data security: Data is contained within networks and apps. A distinct security layer is dedicated to safeguarding business and consumer information.
- Cloud security: A lot of files are stored in virtual settings, or "the cloud." There are several difficulties in protecting data in an atmosphere where everything is done online.
- Security for portable electronics: Almost every form of security problem exists for mobile devices and tablets by themselves.
- Planning for disaster recovery and business continuity is necessary to ensure that operations continue in the case of a security breach, natural disaster, or other unforeseen occurrence. You'll need a strategy for this. end-user instruction Users might be clients using a corporate app or staff using the network. Education on cybersecurity best practices, such as password updates, strong passwords, two-factor authentication, etc., is crucial.
Dicey cybersecurity myths

The number of cybersecurity events is increasing globally, but there are still many misunderstandings, such as the idea that:
- Recognised risks: With thousands of new vulnerabilities being discovered in both new and old apps and devices, the risk surface is really still growing. Additionally, there are more and more chances for human mistake, particularly from careless workers or subcontractors who accidentally compromise customer data.
- Industry safety: Cyber enemies exploit the necessity of communication networks across practically every government and private-sector institution, posing cybersecurity concerns to every business. For instance, ransomware attacks are now affecting more industries than ever before, including local governments and non-profit organisations. Threats to vital infrastructure, supply chains, and ".gov" websites have also escalated.
- Attack vectors are contained: Attacking Linux systems, operational technology (OT), Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and cloud settings are just a slew of possible attacks vectors that cybercriminals are constantly discovering.
Cybersecurity: Why It's Important

Governmental, military, business, financial, and medical entities acquire, process, and store unheard-of amounts of data on computers and other devices, making cyber security crucial. Sensitive information, such as intellectual property, financial data, personal information, or other sorts of data for which illegal access or disclosure might have unfavourable effects, can make up a sizeable amount of that data. In the course of conducting business, organisations transfer sensitive data over networks and to other devices; cyber security refers to the field devoted to safeguarding such data as well as the technology used to handle or store it.

Companies and organisations, especially those responsible with protecting data related to national security, health, or financial records, must take action to defend their sensitive business and personal information as the frequency and complexity of cyber assaults increase. The country's senior intelligence officers warned that cyber assaults and digital espionage pose a greater danger to national security than terrorism as early as March 2013.
New Threats Are Posed by Emerging Technologies

With the inclusion of the advantages of digital computer power to essentially every element of human life in recent decades, the world has witnessed a profound shift. Western society has progressed from single-purpose film cameras, photocopiers, closed-circuit television, and radio-wave-based music broadcast receivers to connected devices sporting the functionalities of all these devices and numerous others — all within a single device. This evolution has occurred in the span of just one generation.
Modern, cutting-edge computing technology models have concurrently appeared, offering enormous possibilities for even advanced technical augmentation of daily life. There are significant information security threats associated with the development of new technologies and the digital transformation of the human experience. This is by no means a complete list of upcoming technologies. Technologies are continually changing, which leads to new information security issues.
Cybersecurity advice: How to defend yourself against cyberattacks

How can people and companies protect themselves against online threats? Here is our top advice for being safe online:
Upgrade your operating system and software: This ensures that you can take advantage of the latest security updates.
Utilize antivirus software to detect and eliminate threats: Security programmes like Kaspersky Total Security do this. To provide maximum protection, keep your software updated.
Employ strong passwords: Ensure that your passwords are difficult to decipher.
Avoid opening email attachments from unfamiliar senders since they can contain viruses.
Clicking on links in emails from shady senders or unfamiliar websites is not advised: This is a typical example of how malware spreads.
Steer clear of utilising public Wi-Fi networks that aren't secure: These networks leave you open to man-in-the-middle assaults.
All I had to say to you about cybersecurity was that. It's very important to keep your documents and data safe nowadays because you never know who is spying on you, isn't it? Happy hunting in the meantime, and I'll meet you in the subsequent post.